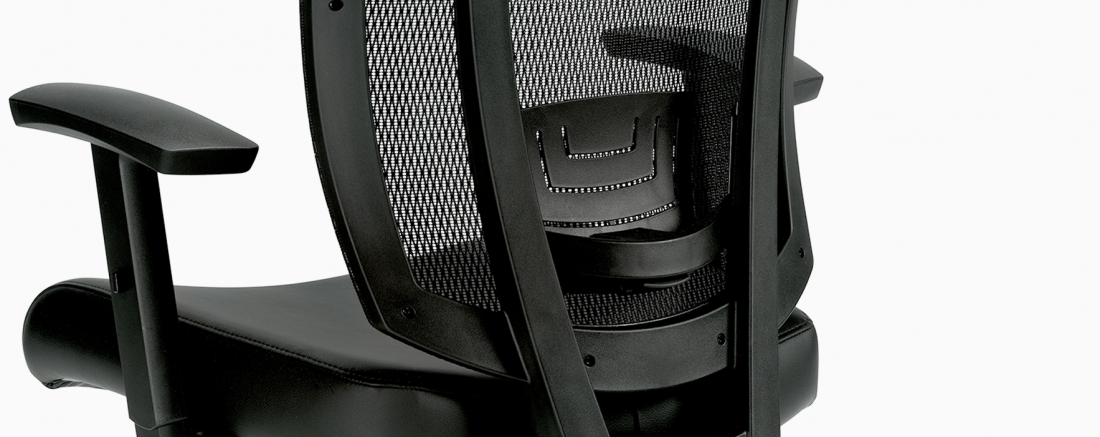
Ergonomics
Promoting Good Posture.
Providing Maximum Comfort.
Maximizing your Ergonomic Seating
- Always select a chair that is designed for the type of work you perform and make certain the chair is comfortable for the length of time spent using it.
- Ensure that the seat and back cushions are contoured to fit your body, which will help eliminate pressure points.
- An ergonomically designed chair should allow changing positions easily.
- As you work, reposition yourself throughout the day to reduce strain and stress on specific muscle groups. If you change job functions, adjust your chair to fit the new task.
- Proper ergonomic seating should help eliminate many of the work related injuries that result from poor posture and poorly designed chairs.
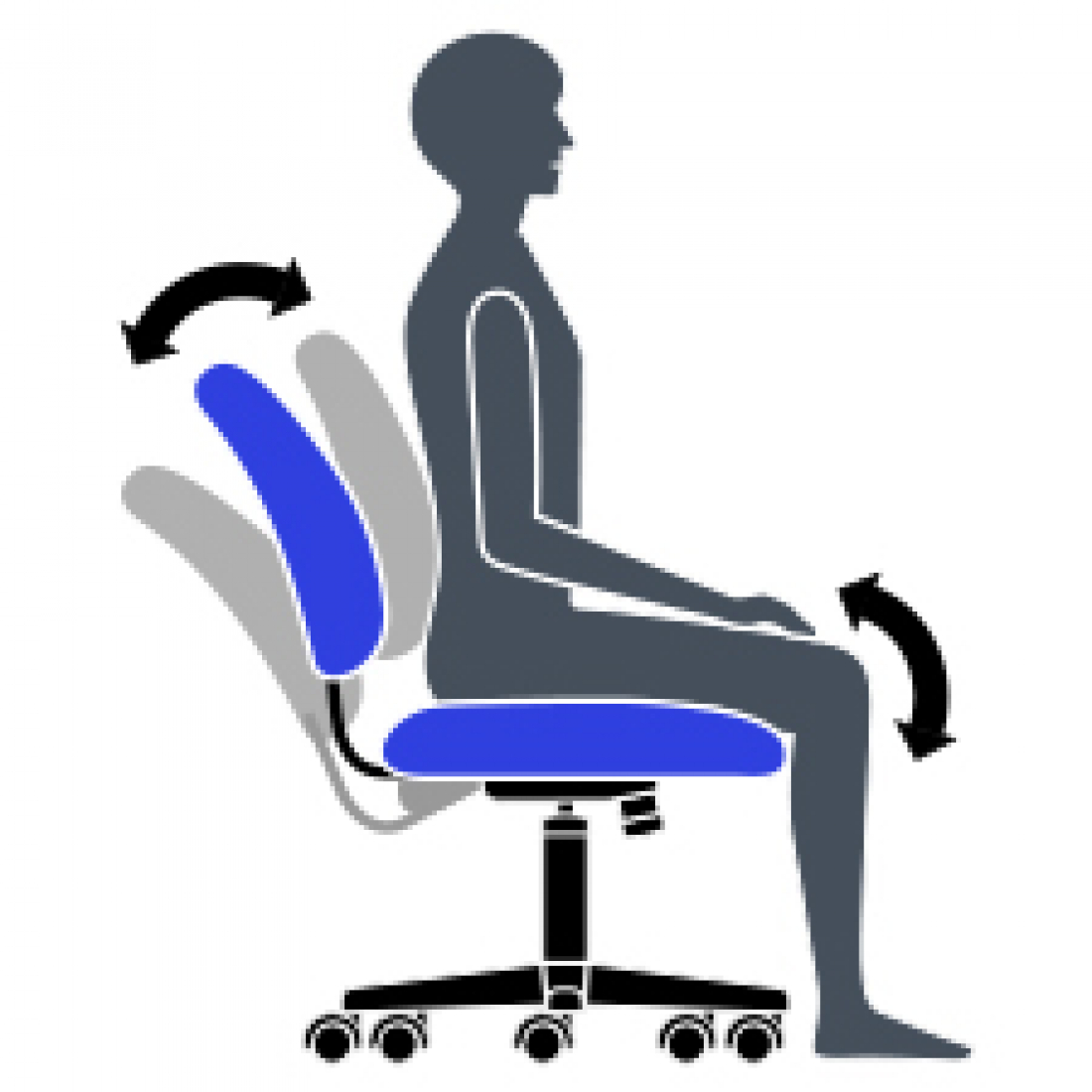

A Tension Adjustment
Increase or decrease to match body weight. Allows you to rock comfortably, without heavy pushing, reducing muscle fatigue.
Increase or decrease to match body weight. Allows you to rock comfortably, without heavy pushing, reducing muscle fatigue.
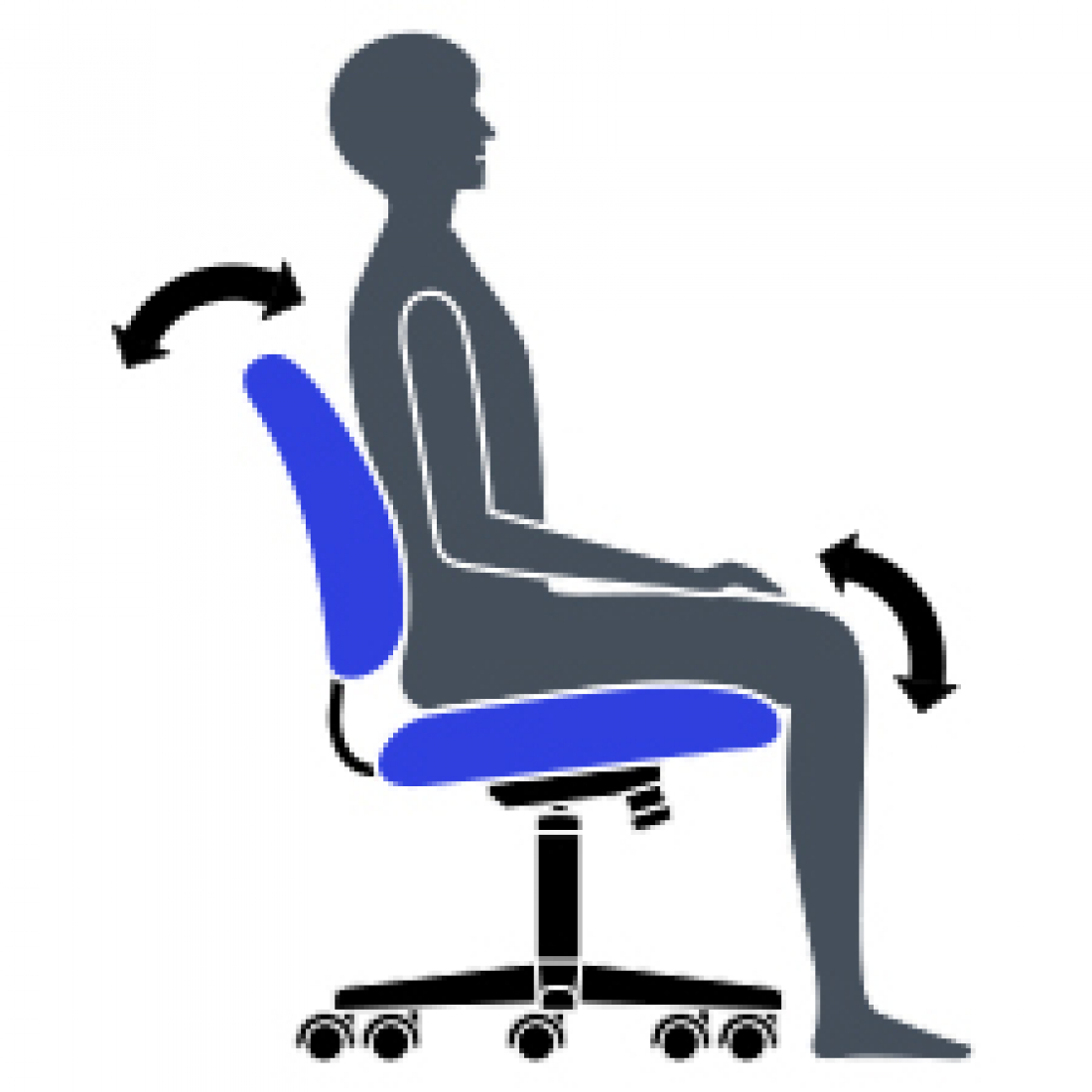

B Chair Tilt Lock
Lock the tilt movement in position(s) to accommodate your working posture. Allows you to lock your chair in a comfortable and supportive position. (Can be either single position, multiple position or infinite position.)
Lock the tilt movement in position(s) to accommodate your working posture. Allows you to lock your chair in a comfortable and supportive position. (Can be either single position, multiple position or infinite position.)
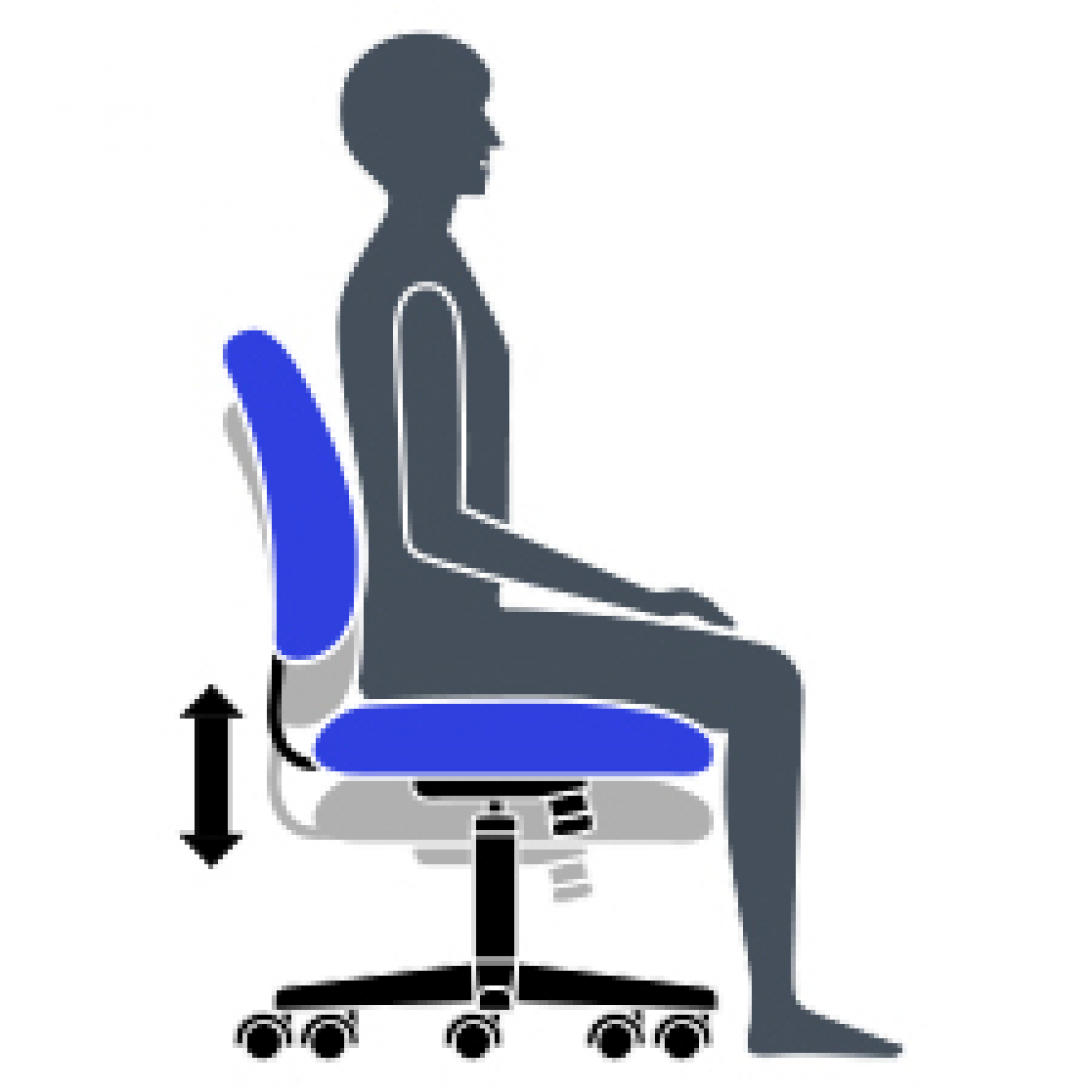
C Seat Height
Raise or lower to allow your feet to rest flat on the floor. Avoids pressure under your thighs, easing blood flow.
Raise or lower to allow your feet to rest flat on the floor. Avoids pressure under your thighs, easing blood flow.
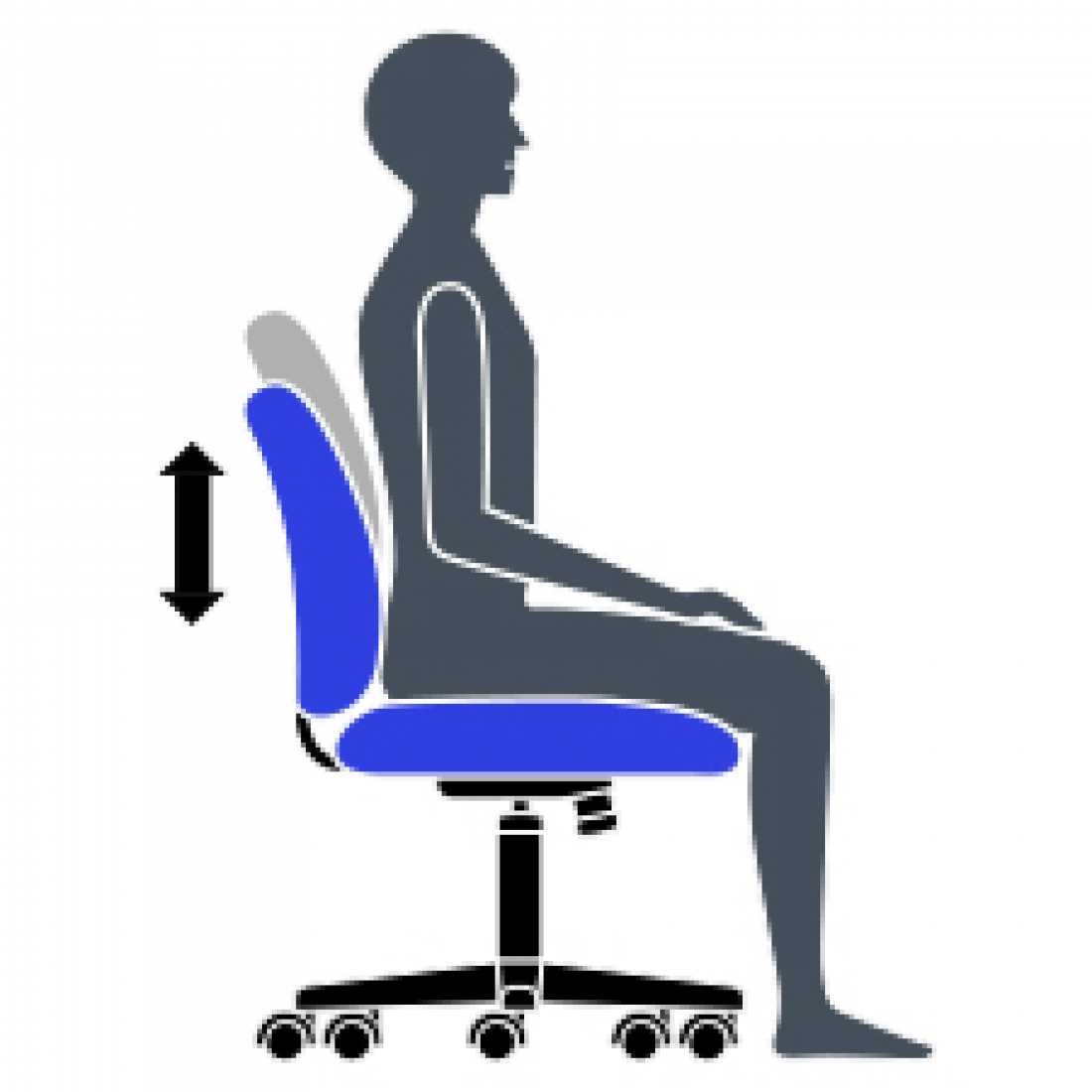
D Back/Lumbar Height Adjustment
Raise or lower to position lumbar support in your lumbar area. Reduces likelihood of back pain.
Raise or lower to position lumbar support in your lumbar area. Reduces likelihood of back pain.
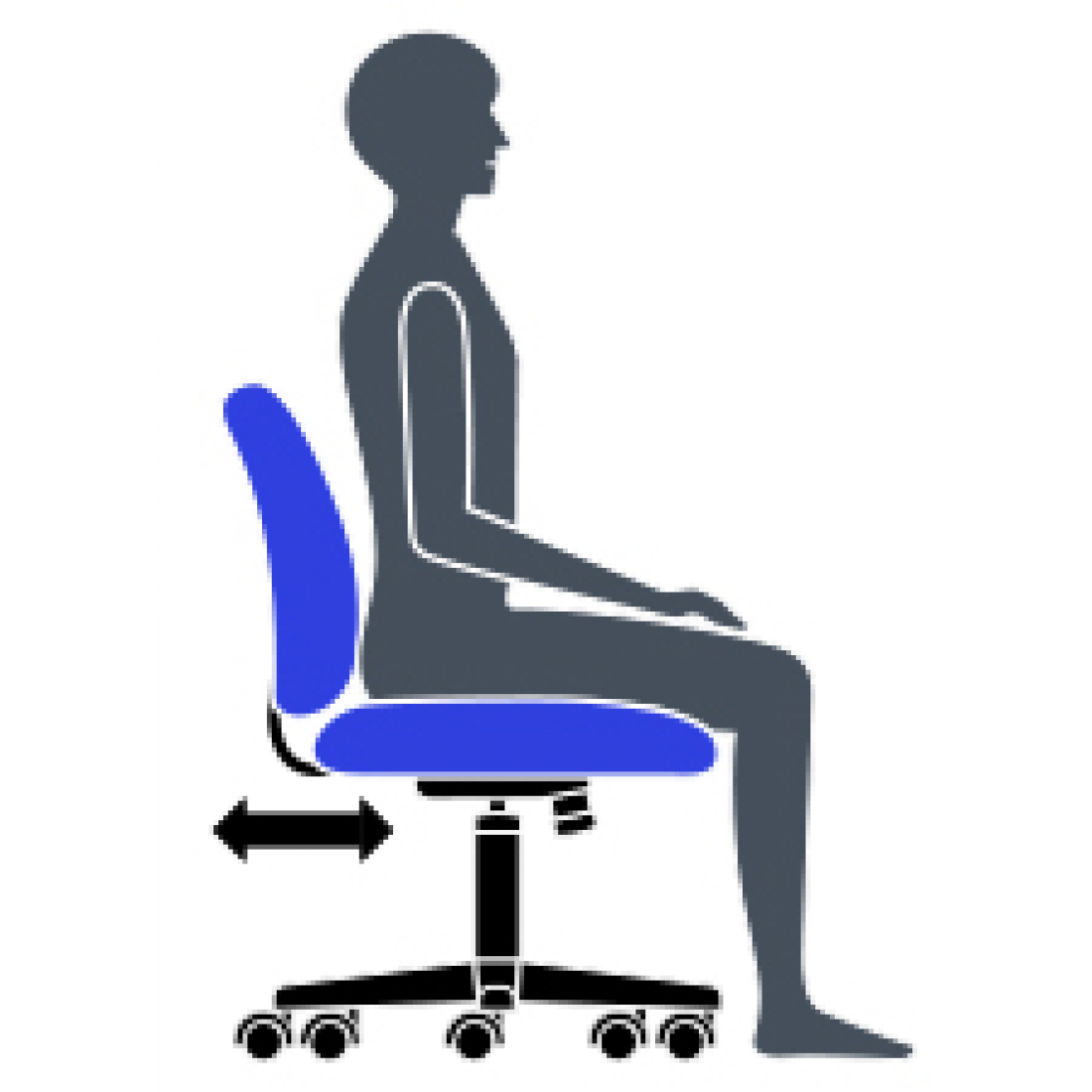
E Seat Depth
Change the depth of the seat to accommodate the length of your thighs. Keeps your back in contact with the backrest while avoiding pressure behind your knees. Can be sliding (MD) or manual.
Change the depth of the seat to accommodate the length of your thighs. Keeps your back in contact with the backrest while avoiding pressure behind your knees. Can be sliding (MD) or manual.
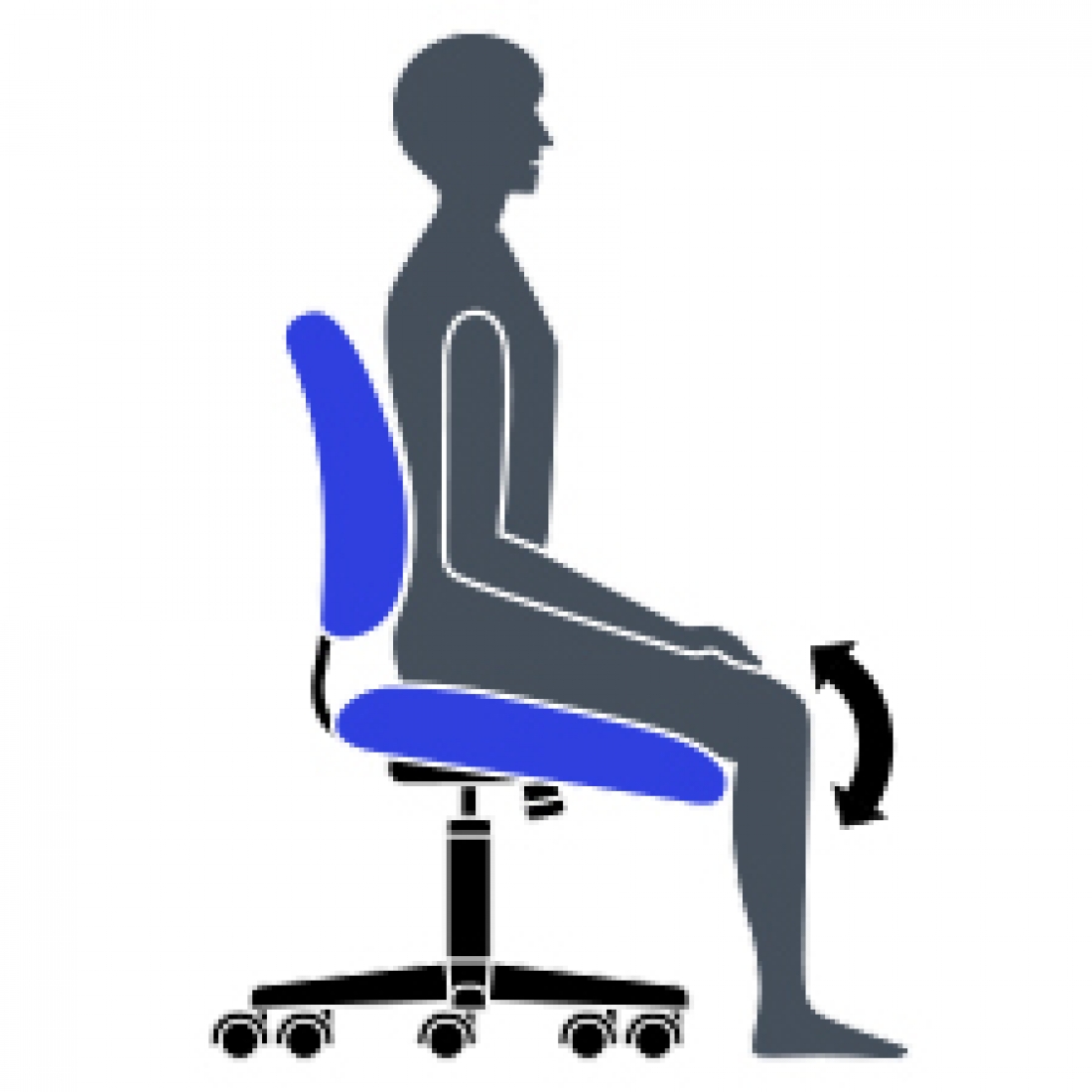

F Seat Angle Adjustment
Allows chair to tilt forward changing the angle of your thighs in relation to the floor. Helps reduce disc pressure during forward leaning tasks.
Allows chair to tilt forward changing the angle of your thighs in relation to the floor. Helps reduce disc pressure during forward leaning tasks.
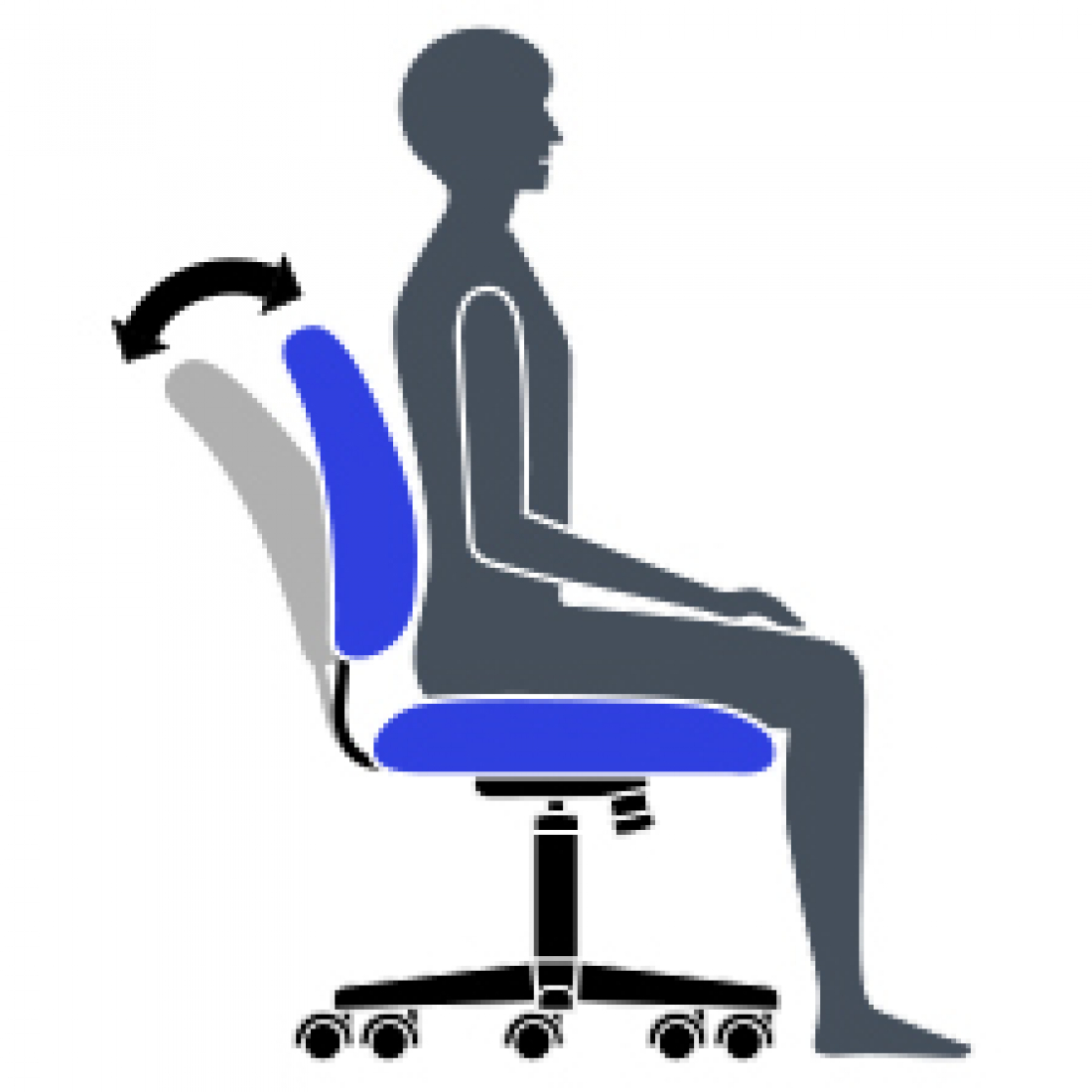

G Back Angle Adjustment
Adjust to change the angle of your torso in relation to your thighs. Helps reduce disc pressure and relaxes your back muscles.
Adjust to change the angle of your torso in relation to your thighs. Helps reduce disc pressure and relaxes your back muscles.
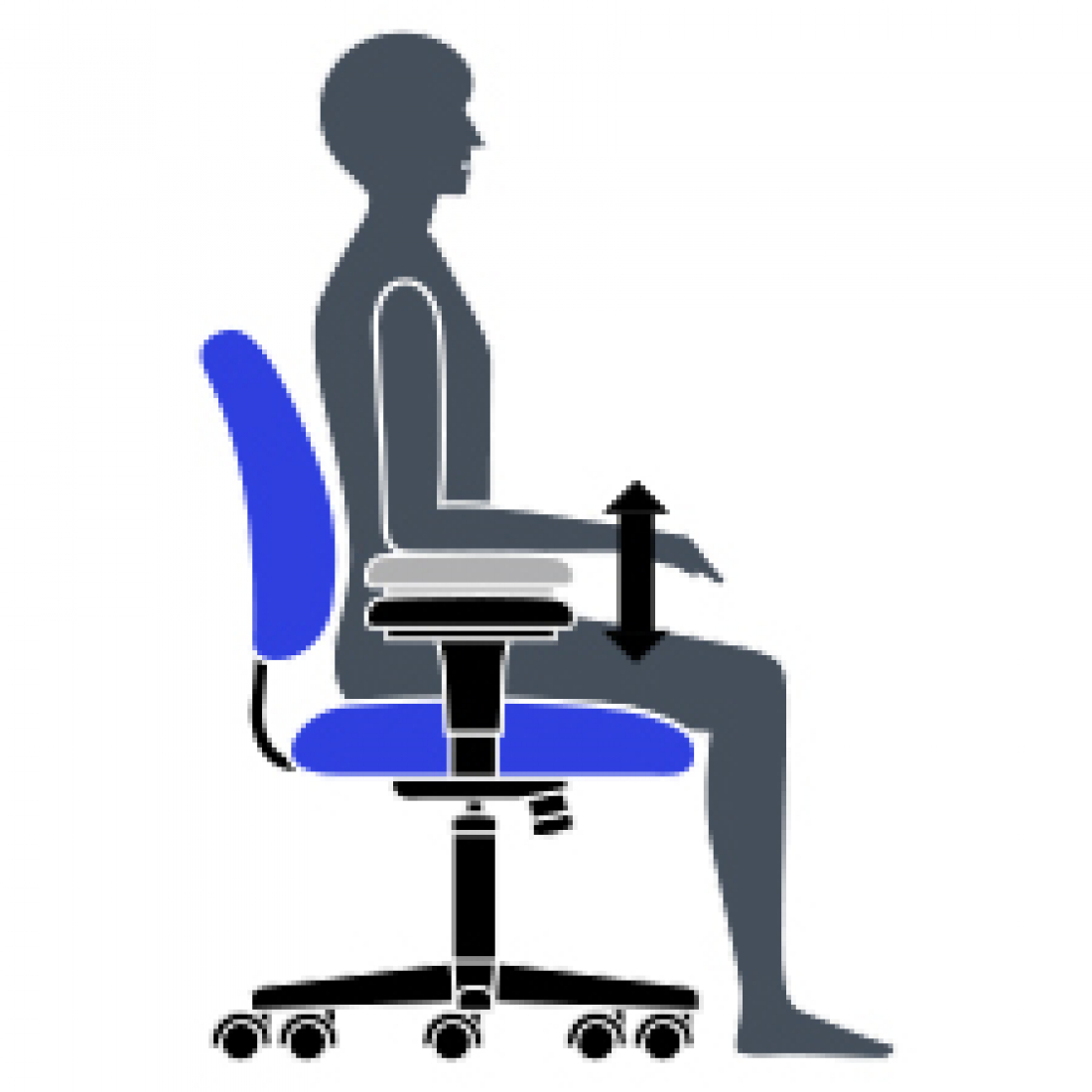

H Arm Height
Raise or lower to support your forearms. Reduces muscular effort in neck and shoulders, minimizing risk of pain.
Raise or lower to support your forearms. Reduces muscular effort in neck and shoulders, minimizing risk of pain.
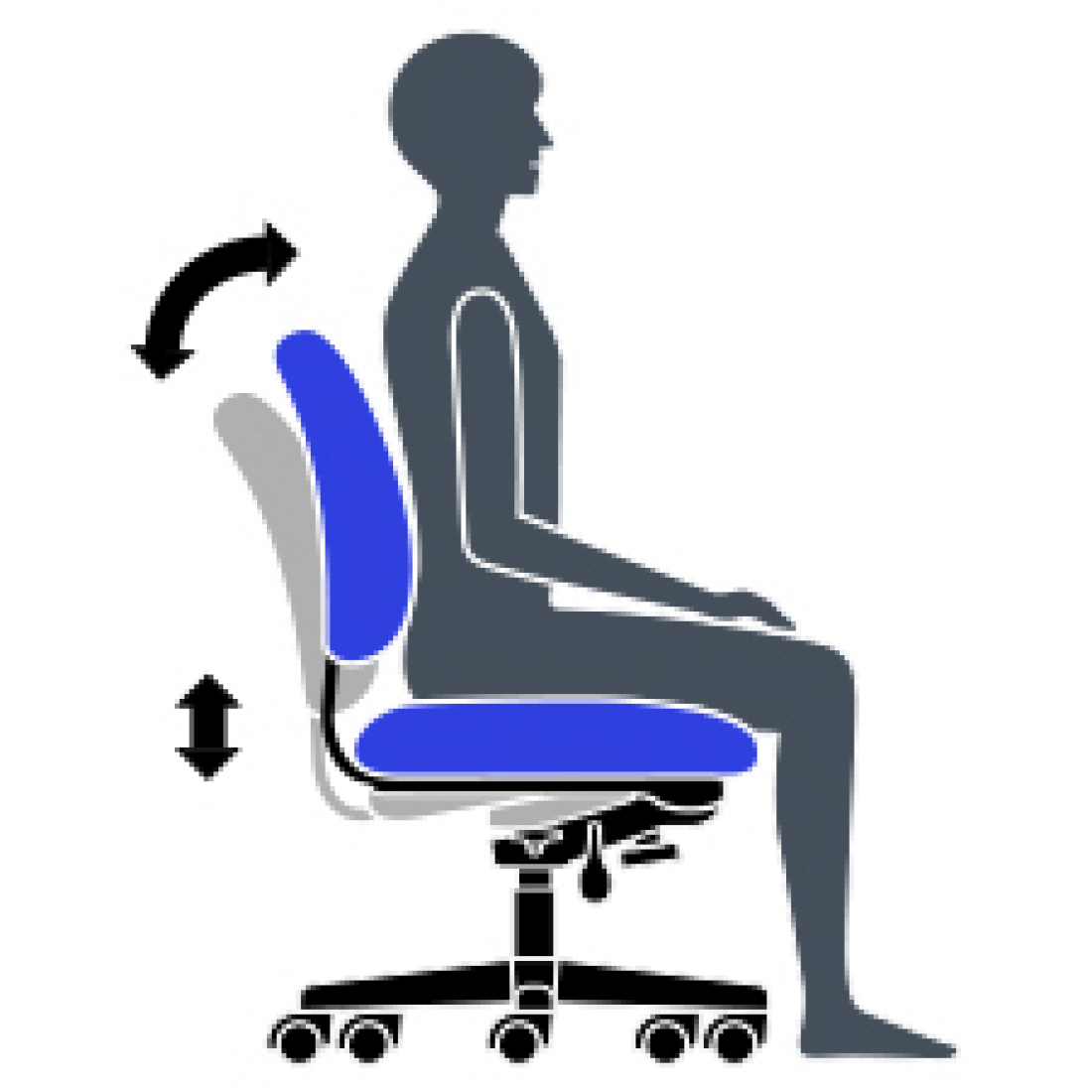
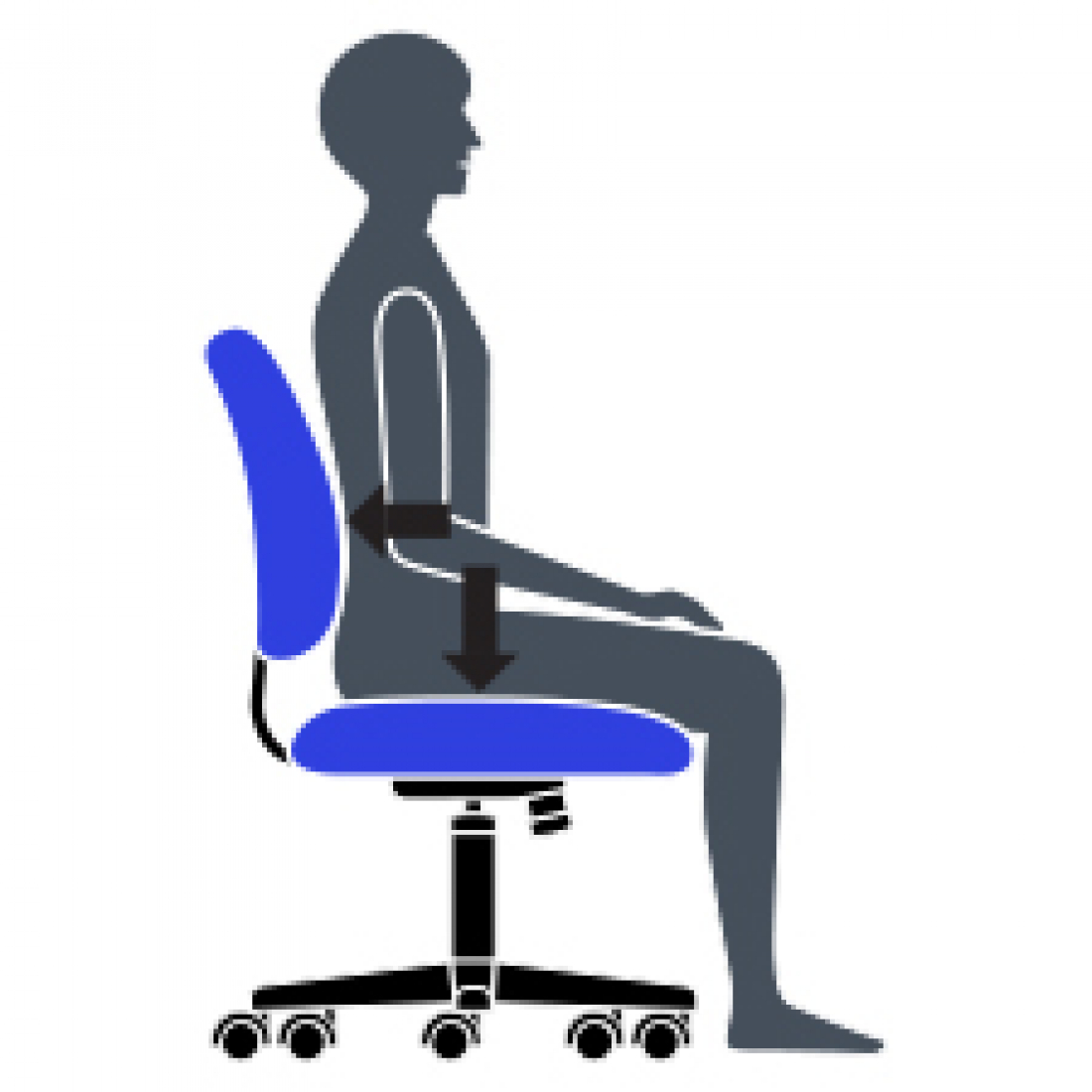
L Synchro-Tilt Movement
Backrest reclines at a faster rate than the seat, increasing the angle between your torso and thighs. Enhances comfort and encourages dynamic body movement.
Backrest reclines at a faster rate than the seat, increasing the angle between your torso and thighs. Enhances comfort and encourages dynamic body movement.
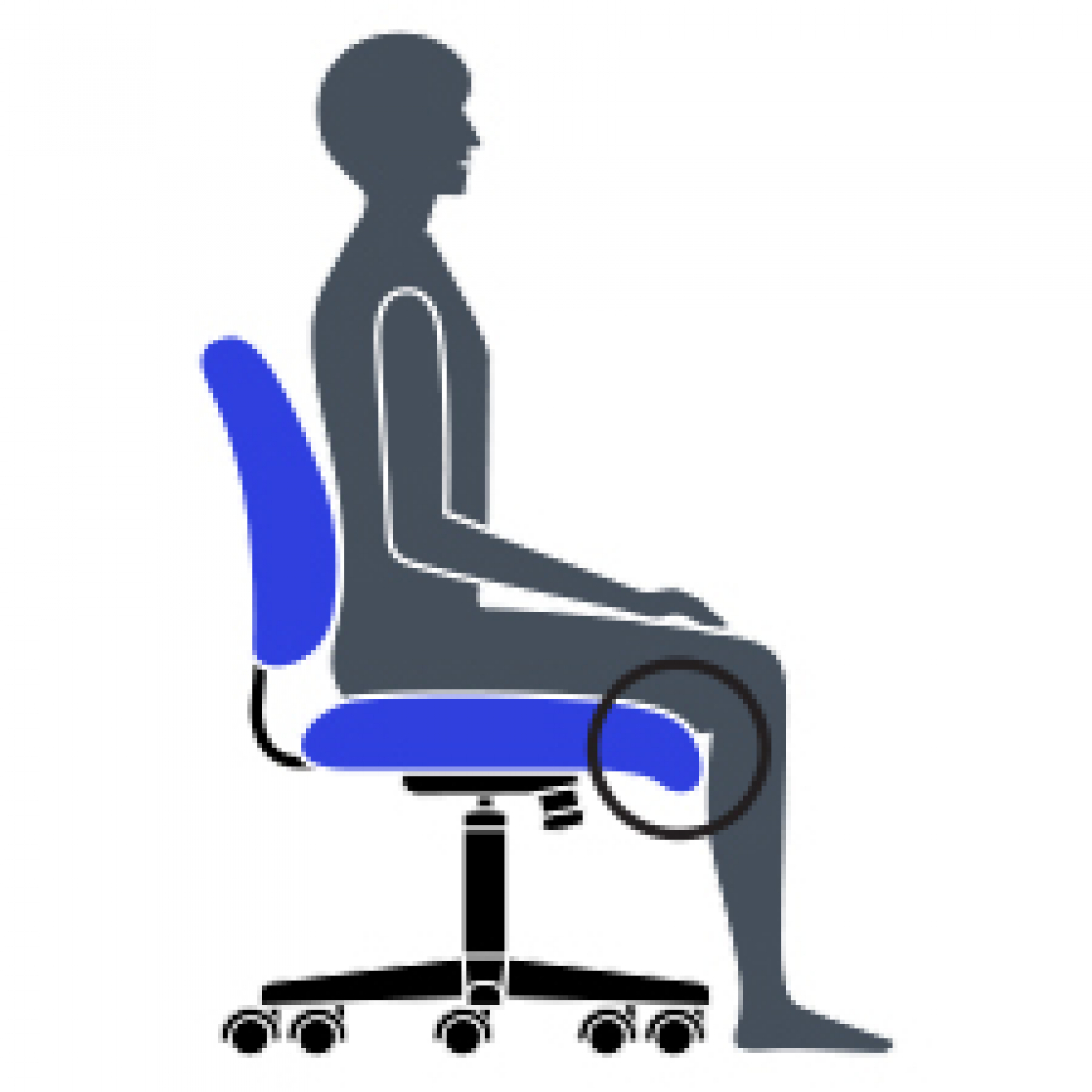

M Waterfall Seat Edge
Reduces pressure at the back of the knee, contributing to good blood flow.
Reduces pressure at the back of the knee, contributing to good blood flow.

N Contoured Cushion
Supports the body effectively, allowing you to sit longer without discomfort.
Supports the body effectively, allowing you to sit longer without discomfort.
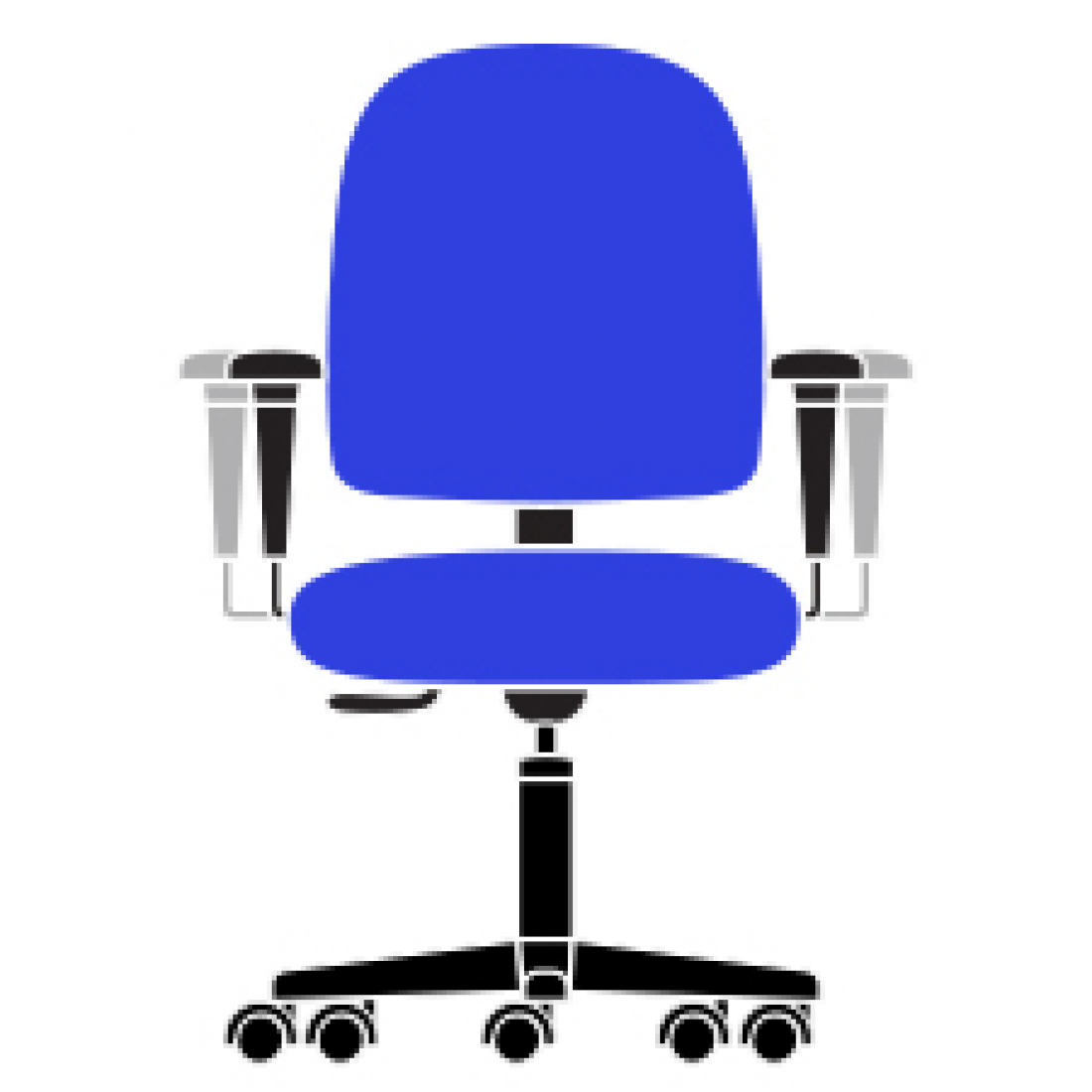

Q Width Adjustable Arms
Allows outward movement of armrests to match shoulder breadth. Ensures armrests properly support forearms, reducing muscular efforts in neck and shoulders.
Allows outward movement of armrests to match shoulder breadth. Ensures armrests properly support forearms, reducing muscular efforts in neck and shoulders.
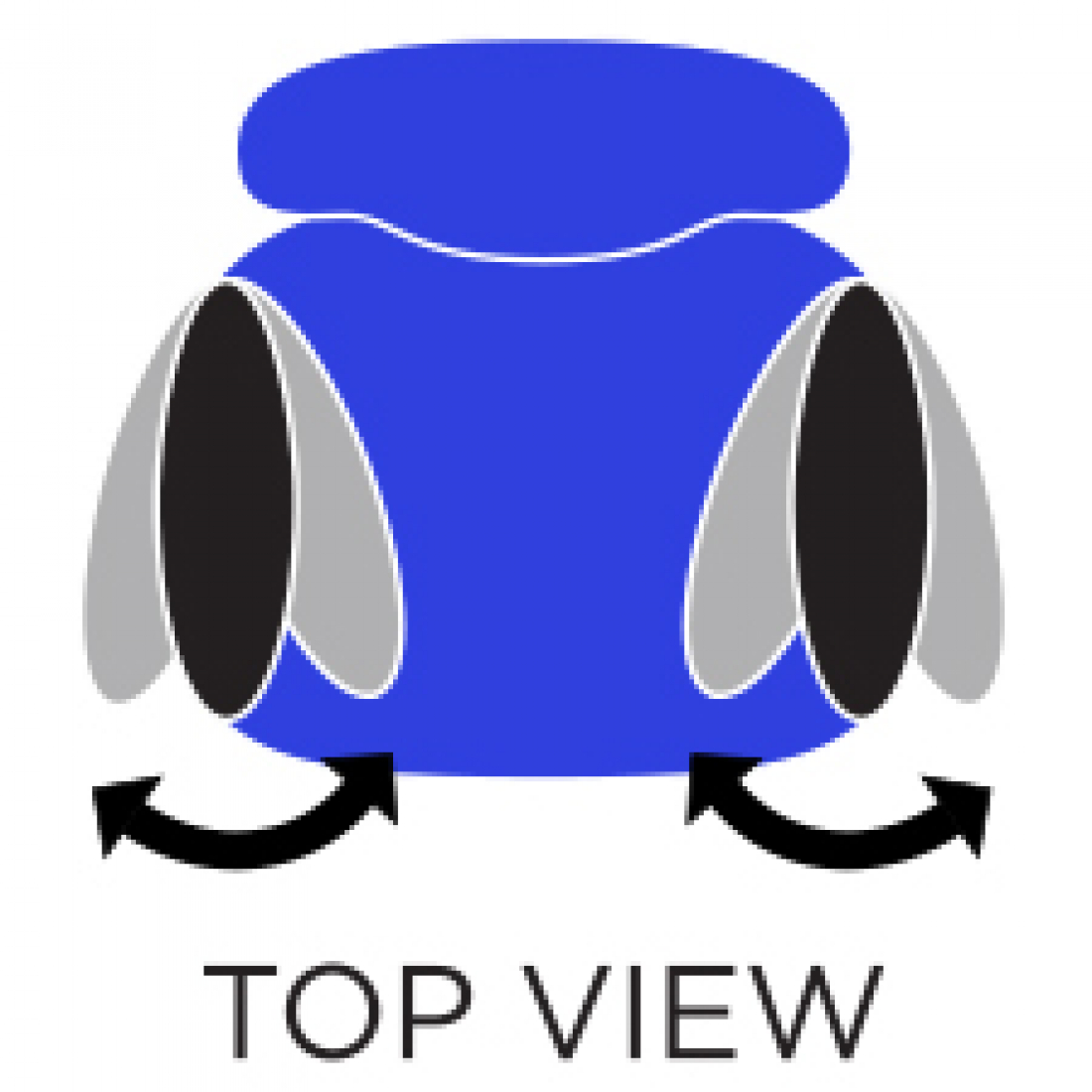

R Arm Rotation
Rotate armcaps to support your forearms in various positions. Reduces muscular effort in neck and shoulders minimizing risk of pain.
Rotate armcaps to support your forearms in various positions. Reduces muscular effort in neck and shoulders minimizing risk of pain.
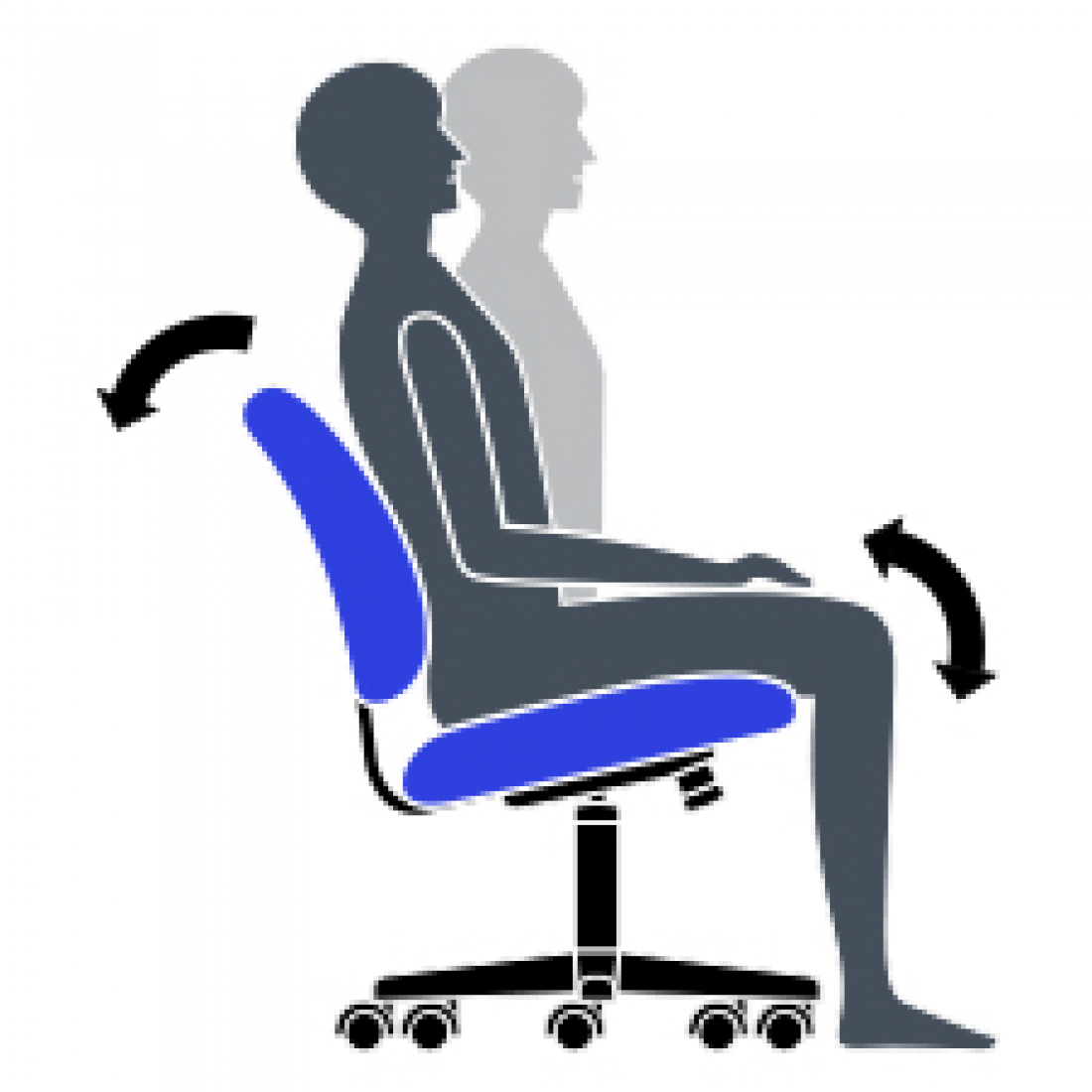

S Center Tilt
Chair tilts from a pivot point under the center of the seat allowing you to rock. When your feet are well supported, blood flow is enhanced.
Chair tilts from a pivot point under the center of the seat allowing you to rock. When your feet are well supported, blood flow is enhanced.
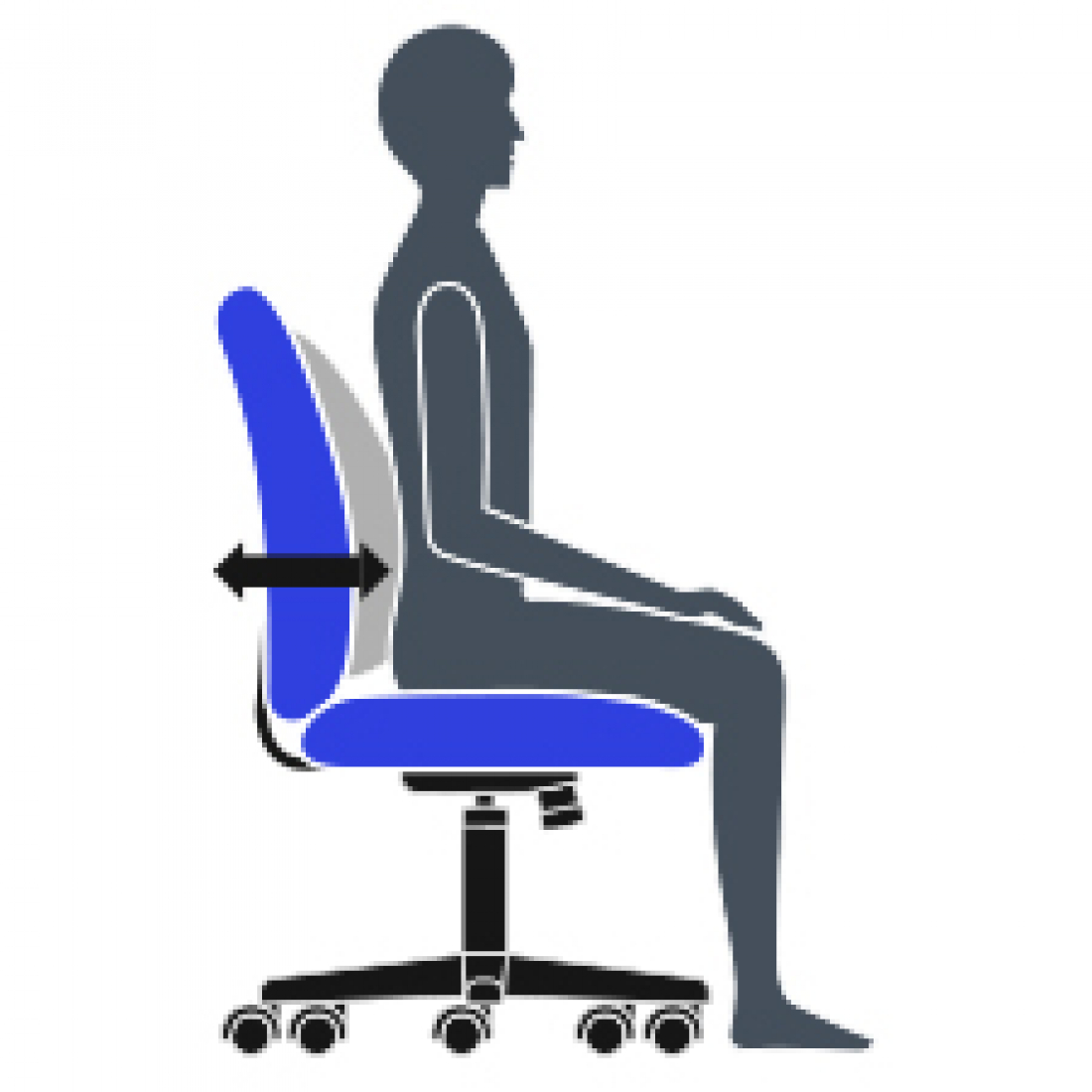

V Lumbar Depth Adjustment
Increase or decrease curvature of the back to match the profile of your lower back. Enhances comfort and support in the lower lumbar area.
Increase or decrease curvature of the back to match the profile of your lower back. Enhances comfort and support in the lower lumbar area.